The development of a smart city can not live without it because it is everywhere ...
With the rise of the concept of smart city, all the major enterprises have laid out the layout around the related fields of smart city. The importance of street lighting as an infrastructure that can be found in cities is self-evident. So, the future of wisdom lighting will bring what changes street? What does it mean to build a smart city? In this article, JüREN HASE, vice president of machine-to-machine competence at Deutsche Telekom AG, Deutsche Telekom AG, said that Smart Street Lights will form the foundation of a municipal network that provides services in parking control, waste management and traffic flow.
The next generation of street lighting will be networked. Cities around the world are already experimenting with smart lighting systems that can be remotely controlled. Not only can the cost of electricity be reduced, but demand-driven lighting can be achieved, reducing carbon dioxide emissions. The current design goes even further: experts see "connected lights" as "nodes" in the smart city's multi-purpose communications network.
Now, the main use of street lights is lighting. However, the future of street lamps will play more functions. For example, when the trash is full, the street light will notify the Garbage Collection Service or record changes in traffic and enter those data into the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). Street lighting will no longer be an isolated area, but part of a networked city infrastructure.
The next generation of street lighting will be networked. Cities around the world are already experimenting with smart lighting systems that can be remotely controlled. Not only can the cost of electricity be reduced, but demand-driven lighting can be achieved, reducing carbon dioxide emissions. The current design goes even further: experts see "connected lights" as "nodes" in the smart city's multi-purpose communications network.
Now, the main use of street lights is lighting. However, the future of street lamps will play more functions. For example, when the trash is full, the street light will notify the Garbage Collection Service or record changes in traffic and enter those data into the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). Street lighting will no longer be an isolated area, but part of a networked city infrastructure.
This vision is based on the emergence of the concept of IoT and smart cities. Every imaginable object and location is networked: cars, containers, streetlights and parking lots, and even watches, glasses and pens. They can measure various parameters in the environment, as well as digitize their daily work. At the core of this change is machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, automatic exchange of data between networked devices or with control centers.
Smart City Solutions are considered key to reducing energy and maintenance costs, meeting regulatory requirements for climate protection and providing better services to citizens. Smart street lamps play a central role in this regard. In fact, in many cities, street lighting accounts for about 20% of public complaints. Intelligent systems can automate the maintenance process. Plus LED, programmable lighting management system can reduce the city's electricity costs by 70%.
Not just artificial light
Machine to Machine (M2M) communication what is it? Here's an example. For example in the industrial field, M2M is used for remote maintenance of machines and equipment. Technicians can see the status of worn parts in the distance. Whenever an error occurs or the system detects a preset pattern, an employee is automatically alerted. This increases the transparency of production, maintenance and resource use. Smart lighting systems provide similar benefits. In order to identify flawed lamps and lanterns, there is no need to rely on night patrols or complaints from citizens, and the system can show the status of networked lighting at the center.
When things around us are smart, they have more functions. For example, in Boston's parks, there are smart benches where citizens can charge smartphones and tablets. At the same time, the park benches also measure environmental elements such as air quality and noise level. Therefore, the function of these benches is not merely to provide seats. They become "charging stations" and "gauges." Similarly, networked street lights are not just electrical appliances for lighting; they are nodes in a multi-purpose network.
The basic structure of intelligent lighting
In order to act as a multi-function network, intelligent lighting solutions must meet what requirements? Its basic structure must conform to the current diversity of market solutions. First, the technician needs to install a luminaire equipped with electronics, either in a small box outside the streetlight or in the luminaire. Or, lamp manufacturers want to integrate the hardware directly. Of course, some older model lights may need to be updated to more efficient LEDs. Once upgraded, these lights can be integrated into a short-range network.
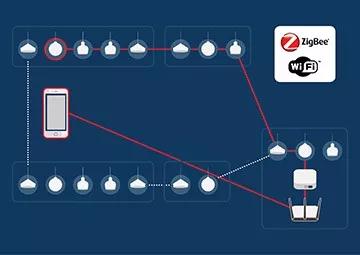
In addition to the hardware in the luminaire, the mobile communication gateway is also used to exchange data over long distances. These can be connected to street lights or placed in the distribution network. Often, they are fixed so that each gateway can reach the maximum number of nodes. Receive information from the node and forward it to the server infrastructure or local server in the cloud. Similarly, the gateway sends control commands back to the node and indicates the switch or dimming.
Smart City "nerve path"
The combination of nodes and gateways creates a two-tier network. Nodes Narrowband networks are used for sensor applications such as smart metering. Gateway Broadband networks are suitable for data-intensive applications such as traffic monitoring with cameras. Mesh networks form the network topology. Each node is thus connected to one or more other nodes. In general, meshed networks are self-healing and therefore highly reliable. Whenever a node fails, the network will automatically forward data through other nodes.
In data transmission, IP standards will be the foundation. Objects and locations have IP addresses so they can be clearly identified. IPv6 Internet Protocol is considered an important prerequisite for the Internet of Things and smart cities. Compared with the previous protocol IPv4, it expands the address space from 232 to 2128 unique addresses, ensuring that network cities have sufficient address space. IPv6 Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Network Protocol (6LoWPAN) is also particularly promising. As an energy-efficient short-range radio technology, 6LoWPAN is especially suitable for sensor networks.
operating system
In addition to data transfer standards, interoperable management system software is also crucial. Most smart lighting solutions provide Web-based portals that allow you to program and manage related lights, such as setting the turn-on and turn-off periods. Once combined with luma and motion sensors, more sophisticated scene modes can be set, such as the darker the sky, the darker the light; in less people the lights turn on only when the motion sensor detects someone passing by.
In order to support more smart city applications, city lighting management software must not be closed and should be scalable through third-party applications. Ideally, cities should implement a management portal that is not limited to applications, and can provide the interface for government agencies, citizens and the private sector.
Need all parties to cooperate
In addition to funding, the hurdle to a smarter city solution is to straighten out relationships. Need different industries cooperation, have different abilities, especially intelligent lighting system. In addition to traditional luminaires and light bulb manufacturers, hardware manufacturers, software vendors and connected service providers are also involved. However, negotiating individual contracts with each participant can be very difficult for the customer - in particular, to ensure that the components used are compatible.
In order to speed up this process, international mobile operators such as Deutsche Telekom will enter the market. This foundation is an extensive network of partners covering all areas of the web ecosystem. For example, the old street lamp is a challenge. In order to upgrade these street lights, specific components and specialized knowledge are required. The partner network includes small companies that specialize in repairing historic street lights and related processes. Cooperation is the key to networked cities, smart street lights is a promising starting point.
link by :www.likeyli.com




评论
发表评论